
Quality assessment of DEM can be performed by comparison of DEMs from different sources. The quality of a DEM is a measure of how accurate elevation is at each pixel (absolute accuracy) and how accurately is the morphology presented (relative accuracy).
Block adjustment from optical satellite imagery. Structure from motion / Multi-view stereo applied to aerial photography. Stereo photogrammetry from aerial surveys. The HRS instrument on SPOT 5 has acquired over 100 million square kilometers of stereo pairs. Later, further data were provided by the European Remote-Sensing Satellite (ERS, 1991) using the same method, the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM, 2000) using single-pass SAR and the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER, 2000) instrumentation on the Terra satellite using double-pass stereo pairs. The SPOT 1 satellite (1986) provided the first usable elevation data for a sizeable portion of the planet's landmass, using two-pass stereoscopic correlation. Other kinds of stereoscopic pairs can be employed using the digital image correlation method, where two optical images are acquired with different angles taken from the same pass of an airplane or an Earth Observation Satellite (such as the HRS instrument of SPOT5 or the VNIR band of ASTER). One powerful technique for generating digital elevation models is interferometric synthetic aperture radar where two passes of a radar satellite (such as RADARSAT-1 or TerraSAR-X or Cosmo SkyMed), or a single pass if the satellite is equipped with two antennas (like the SRTM instrumentation), collect sufficient data to generate a digital elevation map tens of kilometers on a side with a resolution of around ten meters. A DEM implies that elevation is available continuously at each location in the study area. Note that contour line data or any other sampled elevation datasets (by GPS or ground survey) are not DEMs, but may be considered digital terrain models. This method is still used in mountain areas, where interferometry is not always satisfactory. Older methods of generating DEMs often involve interpolating digital contour maps that may have been produced by direct survey of the land surface. Mappers may prepare digital elevation models in a number of ways, but they frequently use remote sensing rather than direct survey data. Some scientists, however, object to vertical exaggeration as misleading the viewer about the true landscape. In these oblique visualizations, elevations are sometimes scaled using " vertical exaggeration" in order to make subtle elevation differences more noticeable. Visualizations are sometime also done as oblique views, reconstructing a synthetic visual image of the terrain as it would appear looking down at an angle. This visualization may be in the form of a contoured topographic map, or could use shading and false color assignment (or "pseudo-color") to render elevations as colors (for example, using green for the lowest elevations, shading to red, with white for the highest elevation.). The digital elevation model itself consists of a matrix of numbers, but the data from a DEM is often rendered in visual form to make it understandable to humans. Relief map of Spain's Sierra Nevada, showing use of both shading and false color as visualization tools to indicate elevation In the following, the term DEM is used as a generic term for DSMs and DTMs. It is possible to estimate a DTM from high resolution DSM datasets with complex algorithms (Li et al., 2005). 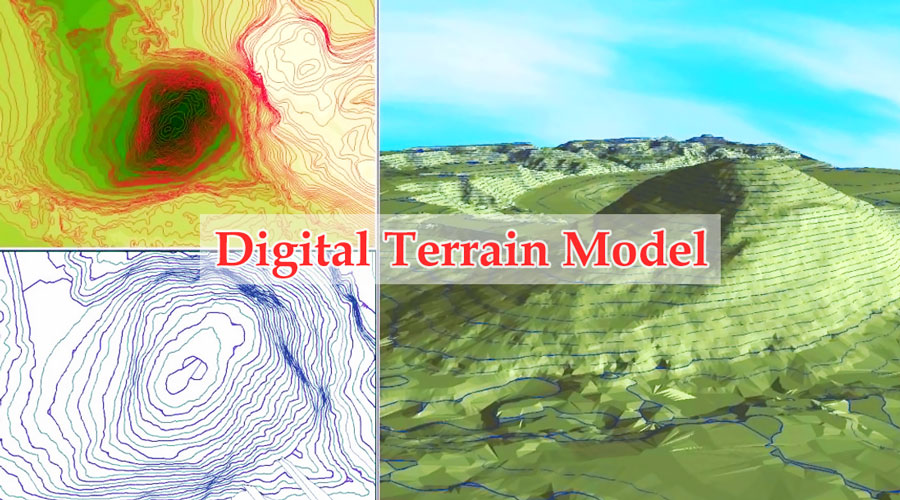
Some datasets such as SRTM or the ASTER GDEM are originally DSMs, although in forested areas, SRTM reaches into the tree canopy giving readings somewhere between a DSM and a DTM). Most of the data providers ( USGS, ERSDAC, CGIAR, Spot Image) use the term DEM as a generic term for DSMs and DTMs.

Other definitions equalise the terms DEM and DTM, equalise the terms DEM and DSM, ĭefine the DEM as a subset of the DTM, which also represents other morphological elements, or define a DEM as a rectangular grid and a DTM as a three-dimensional model ( TIN). ĭEM is often used as a generic term for DSMs and DTMs, only representing height information without any further definition about the surface. In contrast to a DSM, the digital terrain model (DTM) represents the bare ground surface without any objects like plants and buildings (see the figure on the right). In most cases the term digital surface model represents the earth's surface and includes all objects on it.

There is no universal usage of the terms digital elevation model (DEM), digital terrain model (DTM) and digital surface model (DSM) in scientific literature. Digital Terrain Models represent the bare ground. Surfaces represented by a Digital Surface Model include buildings and other objects.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
